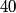 fringes corresponds to a phase difference of fringes corresponds to a phase difference of 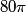 . This must be the phase difference between light that travels . This must be the phase difference between light that travels 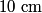 in vacuum and light that travels in vacuum and light that travels 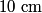 in the gas. Recall that the wavelength of light is reduced a factor of the index of refraction when the light travels through a transparant medium. in the gas. Recall that the wavelength of light is reduced a factor of the index of refraction when the light travels through a transparant medium.Therefore, 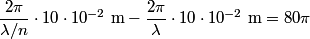 Solving for 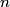 , we find that , we find that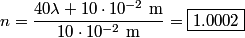 Therefore, the correct answer is (C). |